| Name (External link to a inner body webpage with more info) |
Image (External link to livescience webpage with ore info) |
Functions |
| Integumentary System |
 |
-
Its main function is to act as a barrier to protect the body from the outside world.
-
It also functions to retain body fluids, protect against disease, eliminate waste products, and regulate body temperature.
|
| Muscular System |
 |
-
The main function of the muscular system is movement.
-
Muscles are the only tissue in the body that has the ability to contract and therefore move the other parts of the body.
-
Related to the function of movement is the muscular system's second function: the maintenance of posture and body position.
|
| Skeletal System |
 |
-
The adult human skeletal system consists of 206 bones, as well as a network of tendons, ligaments and cartilage that connects them.
-
The skeletal system performs vital functions — support, movement, protection, blood cell production, calcium storage and endocrine regulation — that enable us to survive.
|
| Nervous System |
 |
-
The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, sensory organs, and all of the nerves that connect these organs with the rest of the body.
-
Together, these organs are responsible for the control of the body and communication among its parts.
|
| Circulatory System/Cardiovascular System |
 |
-
The human circulatory system functions to transport blood and oxygen from the lungs to the various tissues of the body.
-
The heart pumps the blood throughout the body.
-
The lymphatic system is an extension of the human circulatory system that includes cell-mediated and antibody-mediated immune systems.
|
| Lymphatic System |
 |
-
The primary function of the lymphatic system is to transport lymph, a fluid containing infection-fighting white blood cells, throughout the body.
-
The lymphatic system primarily consists of lymphatic vessels, which are similar to the circulatory system's veins and capillaries.
|
| Respiratory System |
 |
-
The function of the human respiratory system is to transport air into the lungs and to facilitate the diffusion of Oxygen into the blood stream.
-
It also receives waste Carbon Dioxide from the blood and exhales it.
|
| Endocrine System |
 |
-
he endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones, chemical substances produced in the body that regulate the activity of cells or organs.
-
These hormones regulate the body's growth, metabolism (the physical and chemical processes of the body), and sexual development and function.
|
| Urinary System |
 |
-
Their function is to remove liquid waste from the blood in the form of urine; keep a stable balance of salts and other substances in the blood; and produce erythropoietin, a hormone that aids the formation of red blood cells.
-
The kidneys remove urea from the blood through tiny filtering units called nephrons.
|
| Male Reproductive System |
 |
-
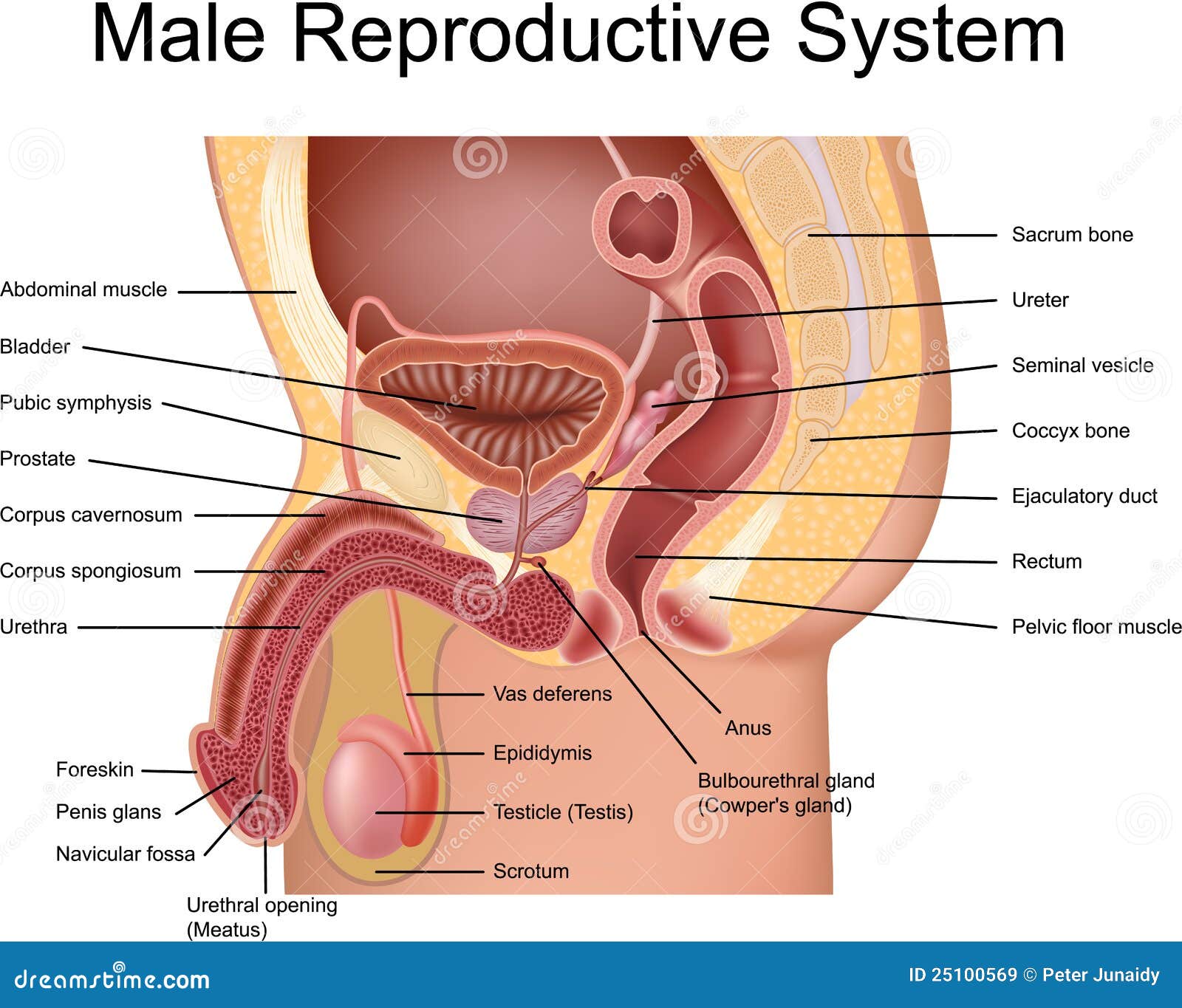
These external structures include the penis, the scrotum, and the testicles.
-
The organs of the male reproductive system are specialized for the following functions: to produce, maintain and transport sperm (the male reproductive cells) and protective fluid (semen) to discharge sperm within the female reproductive tract.
|
| Female Reproductive System |
 |
-
The female reproductive system provides several functions.
-
The ovaries produce the female egg cells, called the ova or oocytes.
-
The oocytes are then transported to the fallopian tube where fertilization by a sperm may occur.
|
| Digestive System |
 |
-
The function of the digestive system is digestion and absorption.
-
Digestion is the breakdown of food into small molecules, which are then absorbed into the body.
-
The digestive system is divided into two major parts: The digestive tract (alimentary canal) is a continuous tube with two openings: the mouth and the anus.
|
| Immune System |
 |
-
The immune system is made up of a network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body.
-
One of the important cells involved are white blood cells, also called leukocytes, which come in two basic types that combine to seek out and destroy disease-causing organisms or substances.
|












